Which Best Describes Heat Loss Through Air Currents
The picture below shows warm air over land and cool air over water. This works in a.
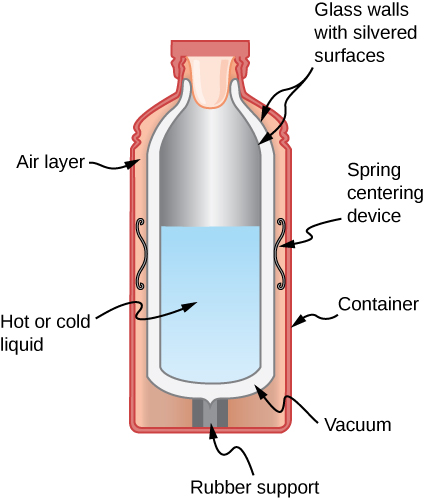
Mechanisms Of Heat Transfer University Physics Volume 2
Not liquid or gaseous.

. The heat absorbed by the atmosphere. Figure 811 Earths heat budget. The heat absorbed by the land and oceans is exchanged with the atmosphere through conduction radiation and latent heat phase change.
If proper measures are not taken to mitigate heat loss immediately after birth the temperature of the newborn could drop by 2 to 4 degrees C within the first 20 minutes. ___ refers to heat conducted through walls ceilings and floors due to a temperature difference between indoor and outdoor air Heat leakage A materials ___ indicated how much heat will transfer through 1Ft2 of the material 1 thick in 1hr when there is a 1degF temperature difference between the two sides of the material. But the best known types are pollutants created by the incomplete burning of oil wood and other carbon-based materials.
Electricity turns to heat air in the oven heats up and the molecules move faster air moleucles bump into the chicken moleules in the chicken move faster. A map view of surface air movement in a low-pressure system is shown. Hot fluids rise up while cold fluids sink down.
Another name for wind. Thermal Of or relating to heat. What is heat loss from skin by air currents passing over it such as a fan.
What best describes the effect on a blood pressure if a cuff that is too large is used. Thus heat transfer is the transfer of heat or thermal energy between physical systems. CThe air gains the same amount of heat energy that the water loses.
Describes an increase in body temperature without a change in the set point of the hypothalamic regulatory center. When land and water absorb the radiant energy. BThe air gains less heat energy than the water loses.
In meteorology A relatively small-scale rising air current produced when Earths surface is heated. The air above the. 22The diagram below shows a sealed container holding 250 milliliters of water at 80C.
AThe air gains more heat energy than the water loses. Radiation does NOT require molecules to travel. Occurs when thermoregulatory mechanisms are overwhelmed by heat production.
The results of experiments 1 and 2 are shown below. The transfer of heat energy in a fluid liquid or gas due to differences in density and unequal heating. Low temperature heat contains very little capacity to do work so the heat is qualified as waste heat and rejected to the environmentEconomically most convenient is the rejection of such heat to water from a sea lake or riverIf sufficient cooling water is not available the plant can be equipped with a cooling tower or air cooler to reject the waste heat into the atmosphere.
65 CHAPTER 2 The notation Tx on the other hand indicates that the temperature varies in the x-direction only and there is no variation with the other two space coordi- nates or time. Air currents in the atmosphere OR a burner causing water to boil in a pot. When a cast iron skillet containing water is placed on a burner convection currents are formed in the water.
Heat loss by __ varies with the temperature of the environment. Convection takes place through advection diffusion or both. In general the atmosphere is warmer near the surface and colder at higher altitudes and under these conditions warm air rises shuttling heat away from the surface.
Heat can travel from one place to another in several ways. Heat loss through the skin to surrounding cooler objects such as clothing. What is heat loss through skin to surrounding cooler object such as clothing.
Straight down over the land B. Electricity turns to heat currents of radiation swirl around the chicken the inside of the chicken warms up heat spreads throughout the chicken B. The air near the center of this low-pressure system usually will.
In general convection is either the mass transfer or the heat transfer due to bulk movement of molecules within fluids such as gases and liquids. Convection currents is the best example of this mode of heat transfer. Radiation is how heat travels through empty space.
An additional 5 percent of incoming solar energy leaves the surface through convection. Using information from the graphs compare the surface in experiment 2 with the surface in experiment 1. Steady versus Transient Heat Transfer Heat transfer problems are often classified as being steady also called steady- state or transient also called unsteadyThe term steady implies no change.
Meanwhile if the temperature difference exists between the two systems heat will find a way to transfer from the higher to the lower system. The material also prevents air circulating inside the cavity therefore reducing heat loss by convection. Solid Firm and stable in shape.
Heat loss from the skin through the air currents passing over it such as a fan. Radiation is the most significant source of heat loss after birth and throughout the rest of development. Up to 24 cash back Convection is how heat travels through fluids liquids and gases.
Heat loss from the skin to surrounding cooler environments. Straight up above the water C. The different modes of heat transfer include.
The convection currents set up in a room with a radiator are shown in the adjoining figure. Evaporate into a liquid. DNo energy is exchanged between the water and the air.
This up-and-down motion is called a convection current. According to the picture above what direction will the air currents most likely move. There are three common modes of heat transfer conduction convection and radiation.
From the land toward the water. Convection current spreads the heat in a circular up-and-down pattern. So when there is a temperature difference between two bodies heat is transferred from the hot body to the colder body.
The direct transfer of heat energy. Determine both the magnitude of the force of friction and the net force on the block that are required to achieve the results shown in the graph for experiment 2. Refers to heat transfer through the circulation of air currents.
Air flow through the room cases convective heat loss. Of all of the solar radiation reaching Earth 30 is reflected back to space and 70 is absorbed by the Earth 47 and atmosphere 23. This is because heat is lost to the surroundings.
Rise and form clouds. Air in direct contact with the sun-warmed ground becomes warm and buoyant. Air currents form due to the uneven heating of Earth.
Warmer less dense molecules move up while the colder ones sink down. Although liquids and gases are generally not very good conductors of heat they can transfer heat quite rapidly by convection. Heat loss through the roof can be reduced by laying loft insulation.
What is Convection. What is heat loss from the skin to surrounding cooler environments. From the water toward the land D.
What is heat loss through normal body functions such as respiration. Squeeze together to form a high-pressure system.
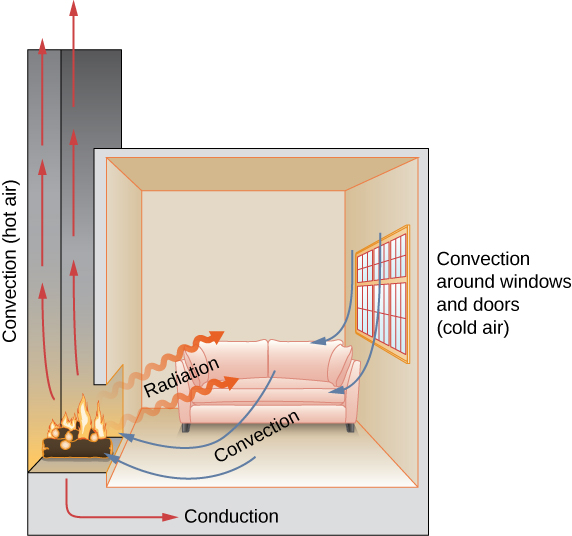
Mechanisms Of Heat Transfer University Physics Volume 2
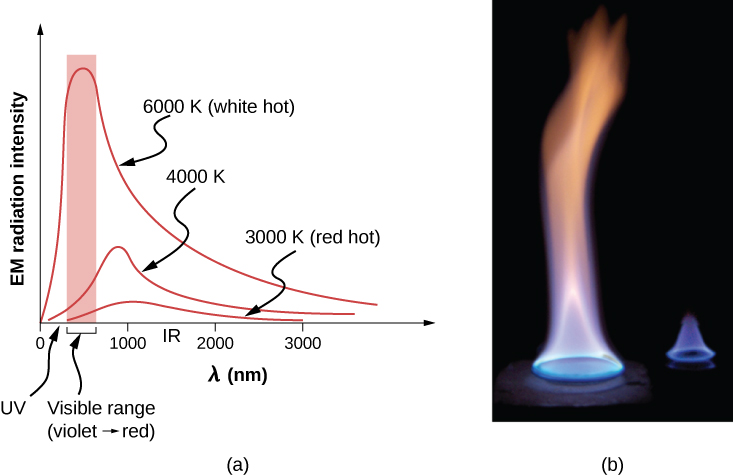
No comments for "Which Best Describes Heat Loss Through Air Currents"
Post a Comment